Webpack is a free and open-source module bundler for JavaScript. It is made primarily for JavaScript, but it can transform front-end assets such as HTML, CSS, and images if the corresponding loaders are included. Webpack takes modules with dependencies and generates static assets representing those modules.
First we start by making our "package.json" file:
npm init -y
Now we install our packages(webpack and webpack-cli):
npm install --save-dev webpack webpack-cli
NOTE: if you see "npm i -D webpack webpack-cli" , it is the same but with their shortcuts
Now in your root make an "index.html" file ,a src folder and a "index.js" inside your src folder ,and a "webpack.config.js" file
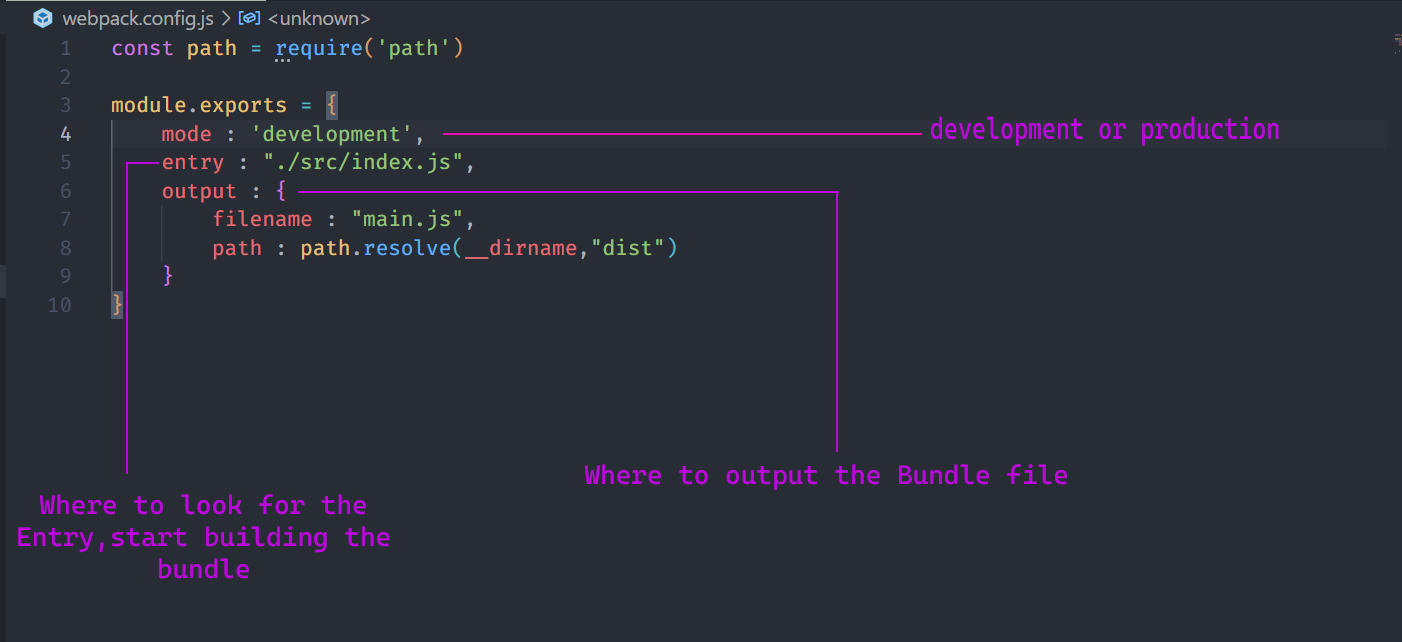
You can think of environments as the context in which your code is running. During development, you're building and running the application on your local machine. Going to production is the process of making your application ready to be deployed and consumed by users.so it means that the files that you work in development must not always be used in production , so webpack makes a "dist" folder that contains the code for out production
make a new script:
"scripts" : {
"build": "webpack --config webpack.config.js"
}
The first command uses webpack and then we tell the webpack to, use the following file as its config
npm run build
we see that a new folder has been added to our root(dist),and inside that, there is a bundle file that we can Link in our "index.html" file